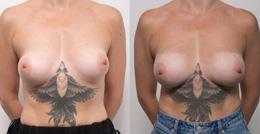
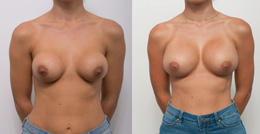
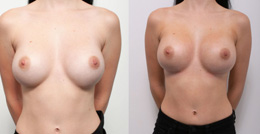
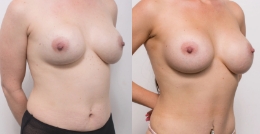
Procedure gallery View our patient results
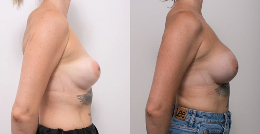
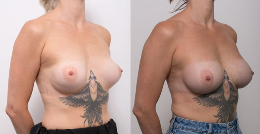
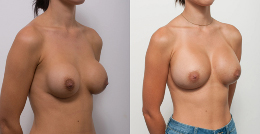
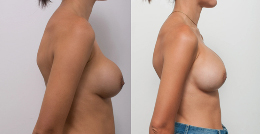

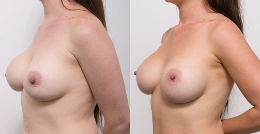
Disclaimer:
The outcomes shown are only relevant for this patient and do not necessarily reflect the results other patients may experience, as results may vary due to many factors, including the individual’s genetics, diet and exercise. Some images may have the patient’s tattoos, jewellery or other identifiable items blurred to protect patient identities.
What is Breast Revision Surgery
Breast revision surgery is performed to address changes or concerns following a previous breast augmentation or reconstruction procedure. This may involve altering, replacing, or removing implants or correcting complications from earlier surgeries. Common reasons for revision include implant rupture, capsular contracture (the hardening of scar tissue around the implant), asymmetry, or changes in implant size or type. Unlike primary breast augmentation, which is performed for the first time, breast revision surgery is undertaken to modify or correct outcomes from prior procedures.
Over time, changes in the body may affect the appearance of breast implants, leading some patients to consider revision. This procedure can be used to adjust breast shape and size after implants have been in place for several years. Whether due to physical changes, complications, or a preference for a different outcome, breast revision surgery allows for adjustments to suit the patient’s current needs. The approach to revision varies based on the specific concerns being addressed, and a consultation is necessary to determine the most suitable options.
At Dr Eddie Cheng’s clinic, breast revision surgery is approached with a focus on addressing individual concerns while prioritising patient safety. The procedure is performed to modify, replace, or remove implants as needed, considering both anatomical factors and the patient’s current preferences. Every case is unique, and a thorough consultation allows for a clear understanding of the concerns and surgical options available.
The consultation process provides detailed information about the potential risks, benefits, and expected changes following surgery. Each surgical plan is tailored to the patient’s needs, ensuring that the chosen approach is suitable for their anatomy and circumstances. The aim is to achieve changes that align with the patient’s requirements while maintaining proportion and balance. A structured plan for aftercare and recovery is also provided to support the healing process and long-term outcomes.
